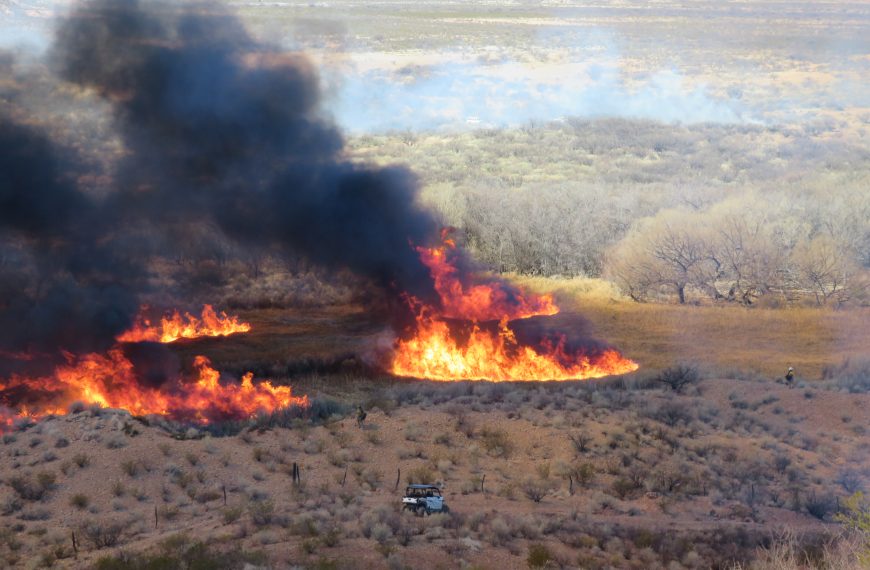
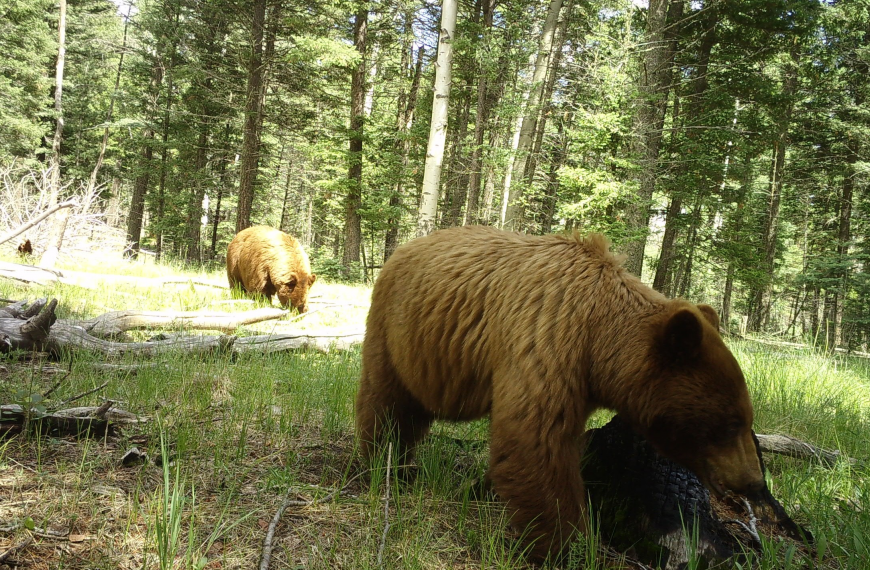
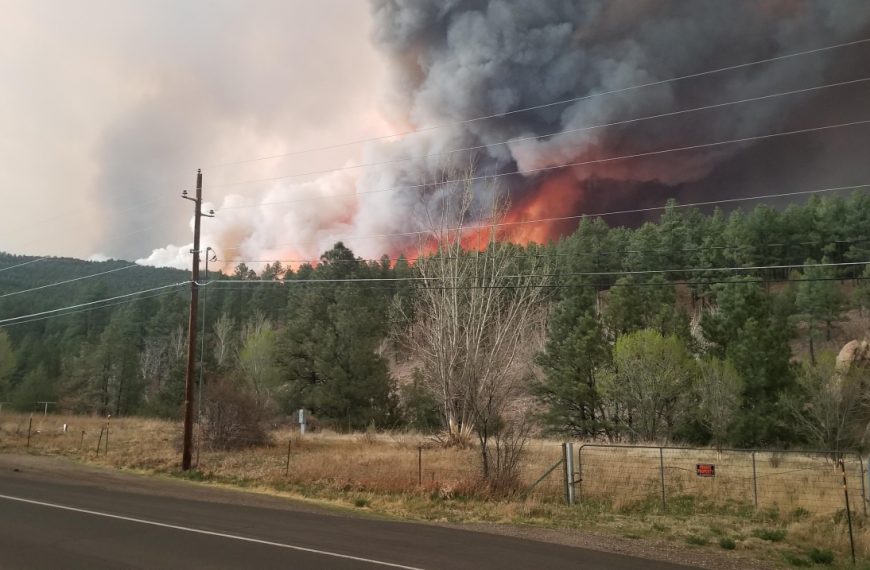
Do high severity burns lead to conversion to new forest types or a shift from forests to shrublands or grasslands? How do wildlife respond to changing habitats? And, finally, what do these changes tell us about how these ecosystems will respond to climate change? We visited the sites of the 2000 Pumpkin Fire and 2003 Aspen Fire, and talked to researchers who have been studying how forests and wildlife respond to high severity burns. View the YouTube video here.
World of Wildland Fire – Intro to Wildland Fire Videos
This series of videos serves as an introduction to wildland fire and has been produced through the Wildfire Education & Training Collaborative (WETC). More in-depth videos will be added as they become available. WETC Mission Statement: To develop multiple sources of media, including but not limited to books, videos and classroom exercises, for the purpose …
Read more “World of Wildland Fire – Intro to Wildland Fire Videos”
Keeping Fire on the Ground: Resource Specialist Perspectives on the Kaibab National Forest
The importance of fire in many western ecosystems cannot be overstated. On the Kaibab National Forest, fire provides habitat for wildlife, maintains watersheds, and supports forest health and productivity. Fire also influences a wide range of values, resources, and ecosystem services. On the Kaibab, resource specialists have a strong understanding and appreciation for the benefits of fire, and they work closely with the fire staff to ensure that fire management and resource management are one in the same. View the YouTube video here.
The New Normal: Wildfire in the 21st Century
The New Normal: Wildfire in the 21st Century, is intended for public use. It explains current issues as they relate to fire management and what managers are doing to help build resilient landscapes. Please share widely and help spread the message about positive fire management.
There is growing recognition that many forests need fire to thin dense vegetation that chokes forest health and creates favorable settings for more destructive fires. Also, climate change has produced hotter, drier weather across the West, and this has directly led to more extreme wildfire behavior over the past few decades. View the YouTube video here.
The 2014 San Juan Fire: Fuel Treatments and Fire Management
The San Juan fire ignited on June 26, 2014 on the White Mountain Apache Reservation and quickly entered the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest. The fire was wind-driven for the first few days, and fire behavior was influenced by extremely dry fuel conditions related to long-term drought. However, as the fire moved to the southwest it encountered a series of fuels treatments done as part of the White Mountain Stewardship Contract and a habitat improvement partnership project. View the YouTube video here.
Related Content
San Carlos Apache – Building a Culture of Fire
For the past decade, the San Carlos Apache fire and forestry staff has been working to reintroduce fire to the landscape through an expanding prescribed fire and managed wildfire program. Stephen J. Pyne narrates this video describing the 2014 fire season on San Carlos when the new approach to fire was tested with the simultaneous management of multiple prescribed burns as well as a number of wildfire starts. One of those starts, the Skunk Fire eventually grew to over 73,000 acres.
Related Content
Every Fire is an Opportunity to Treat a Landscape
On the afternoon of May 20, the Slide Fire was reported towards the south end of Oak Creek Canyon between Flagstaff and Sedona, Arizona. The canyon is steep and rugged – not the type of country that firefighters prefer for taking on a fire directly. After the initial threat to nearby homes passed, fire managers decided to use a confine-and-contain strategy, drawing a large box around the fire perimeter and using low-intensity burnout operations to rob the main head of the fire of fuel. This video describes the how fire officials managed the Slide Fire, and how the chosen tactics lessened negative impacts to the forest and watershed while providing for the safety of the more than 1,200 firefighters working the fire. The indirect tactics used on the Slide Fire are part of a national trend, wildfires being managed in ways that can benefit the landscape even while actively accomplishing suppression and protection objectives. National and regional fire experts discuss these changing trends and how fire management can be further improved to lessen negative impacts and actually create benefits for ecosystems.
Click here for an accompanying “Every fire is an opportunity” write up containing more detail.
The Fire Laboratory: Forest Restoration on the Gila
Vast stands of ponderosa pine stretch across the Gila National Forest, a testament to the role of fire in this corner of the Southwest. For decades, fire managers on the Gila have been reintroducing fire back on to the landscape. This video introduces some of the people behind the story of fire on the Gila National Forest.
Click here for accompanying “The Fire Laboratory” write up containing more detail.
Related Content
Past Meets the Present: Using Old Burns in Fire Management
Over the past two decades the size of wildfires has dramatically increased across the Southwest. These large burned areas have become so common that newer wildfires are burning into and around them. Fire managers increasingly use these previous burns as treatments that either stop or slow fire spread. The interaction of past and current wildfires has important management and ecological consequences.
Click here for accompanying “Past meets the present” write up containing more detail.
Related Content
Mastication Treatments in Southwestern Forests
Video describing mastication fuel treatments in the Southwest. Covers treatment effectiveness during recent large wildfires and also describes the benefits and potential drawbacks of mastication fuel treatments.
Click here for accompanying “Mastication” write up containing more detail.